Last Update: November 15, 2019
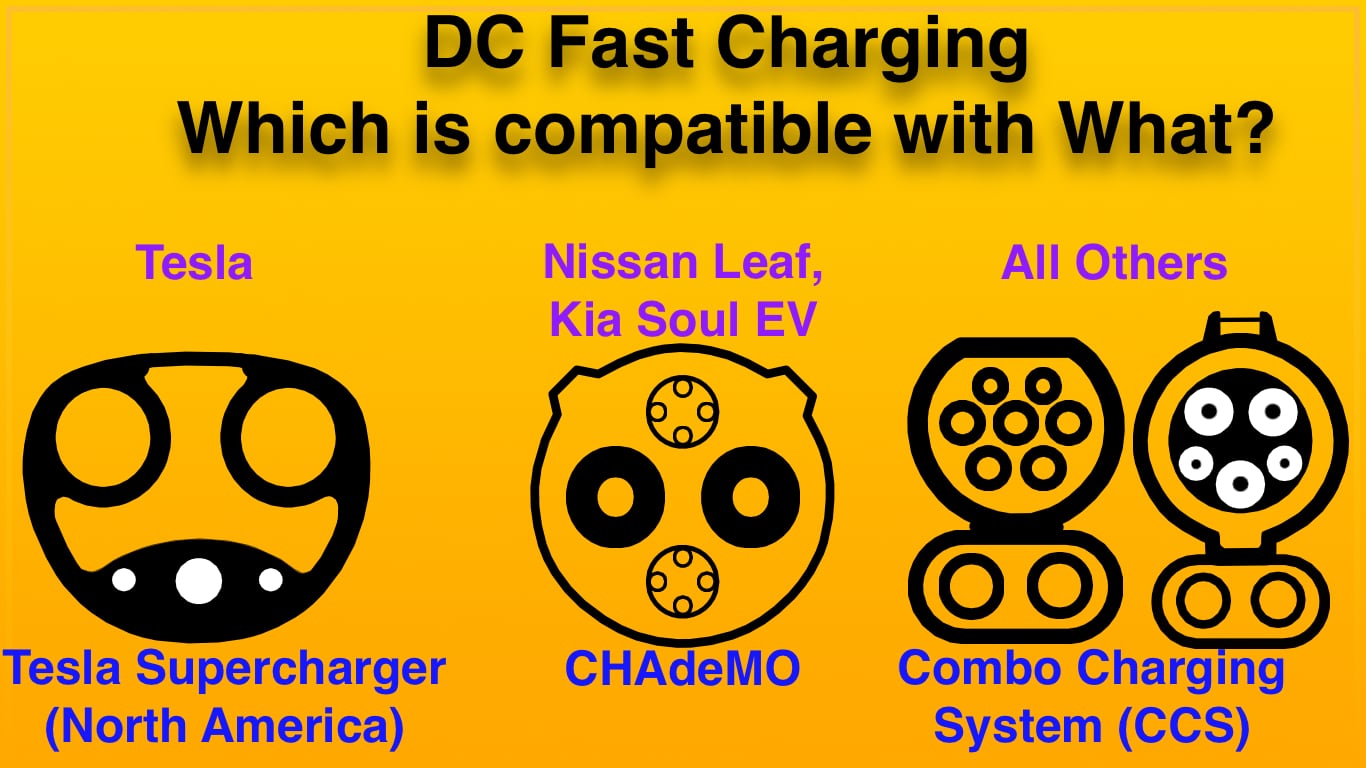
The key to determining if a charging station is compatible with your car is comparing the shape of the charging plug versus the shape of the charging socket on your electric car. If the plug doesn't fit you can't charge - to paraphrase a famous statement from the OJ Simpson trial.
The primary incompatibility is between Tesla and non-Tesla cars. For AC charging every electric car is able to use the public charging network, since Tesla provides an adapter with every car sold. It is in DC fast charging where the most incompatibility exists. Some cars use CHAdeMO, a Japanese fast charging standard primarily used by the Nissan Leaf. Others use the Combo Charging System (CCS), a charging standard used by most of the other automakers. In some markets Tesla uses a proprietary charging connector at Supercharger stations, and charging a Tesla car with a non-Tesla DC fast charging station requires an adapter. In other markets Tesla Supercharger stations have CCS plugs, and in those markets Tesla cars can be charged at CCS charging stations with no adapter. Nowhere does Tesla allow non-Tesla cars to use Supercharger stations.
That was a lot for one paragraph. In the following sections we'll break out in more detail the state of DC fast charging compatibility. For the full story see: Types of electric car charging connectors, and compatibility: A Field Guide to electric vehicle service equipment
AC charging for electric cars
AC charging is what folks typically call "level 1" or "level 2". AC is of course the kind of electricity we typically use for refrigerators and computers and other normal electric devices. For most purposes, AC charging is fully compatible between all car brands. The J1772 charging protocol is used in all regions, but there are two charging connectors - the SAE J1772 connector, and the IEC Type 2 connector. Every electric car implements one of those connectors.
That is, every electric car other than Tesla. In some markets Tesla uses a different charging connector, the proprietary Supercharger connector, and supplies a J1772 adapter to use that connector.
This table shows the connectors used for AC charging. We need to know about these since some AC charging connectors formed the basis of the Combo Charging System DC fast charging connectors.
| Charging Connector | Discussion |
|---|---|
 |
This is the standard SAE J1772 AC charging connector used in North America and many other countries. The good news is every electric car - except for Tesla's - in certain countries use this charging connector. Any electric car with this charging connector will usable at a large number of charging stations. |
 |
In many markets Tesla uses this connector for both AC charging and DC fast charging (Supercharger). This one little connector supports a wide range of charging modes, but it is incompatible with all other charging connectors. In other markets Tesla uses charging connectors standard for that market, such as the IEC Type 2 and Combo 2 connectors in Europe. |
 |
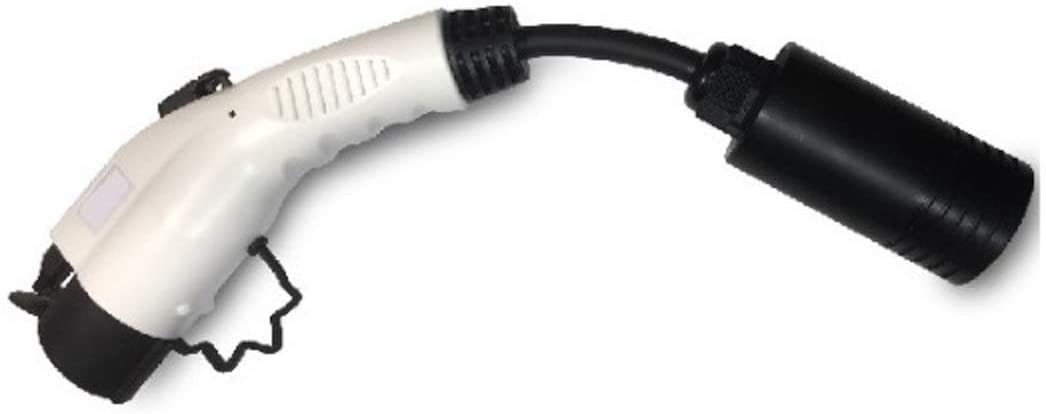
In markets where Tesla uses that connector, this adapter is supplied with all Tesla cars. It lets a Tesla car use a standard SAE J1772 charging station. In markets where Tesla uses a standard charging port, no adapter of this sort is required. |

|
The TeslaTap allows a car with an SAE J1772 charging port to use a Tesla AC charging unit, the Mobile Connector, the Wall Connector, or a Destination Charger. It does not support use with Supercharger stations. |
 |
In Europe, the same J1772 protocol is used through this other connector, the IEC 62196 type 2 plug. This connector is being adopted in most of the world, and it supports single phase AC charging, three phase AC charging, and a couple DC fast charging modes. Initially in Europe there was no standard AC charging connector, but now this connector is the standard. Even Tesla is using this charging connector in markets where it makes sense to do so. This means every electric car in Europe and several other regions can use this widely available AC charging connector. |
DC fast charging of electric cars
In DC fast charging the charging station connects directly to the battery pack. One result is a high charging rate letting the car recharge more quickly. Where the J1772 protocol provides harmony for AC charging, and car owners have little compatibility worry over AC charging connectors, we cannot say the same for DC fast charging of electric cars.
This table demonstrates that in North America the J1772 plug formed the basis of the Combo 1 CCS plug, and in other regions the IEC Type 2 plug formed the basis of the Combo 2 CCS plug.
| Charging Connector | Discussion |
|---|---|
 |
The CHAdeMO standard was developed by TEPCO (Tokyo Electric Power Company) and first deployed in Japan in 2008. The CHAdeMO association oversee's its development, and CHAdeMO has been blessed as an IEC standard. It has since been deployed worldwide primarily thanks to the spread of the Nissan Leaf. A relative handful of electric cars support CHAdeMO. The connector is the same across the world. |
 |
The CHAdeMO charging connector only supports DC fast charging. Therefore an electric car requires a second charging port to support AC charging, using a normal J1772 port. |
 |
In some markets Tesla uses this connector for both AC charging and DC fast charging (Supercharger). In DC mode this connector supports a 120 kiloWatt or more charging rate. |
 |
Tesla makes this adapter allowing Tesla cars made with the North America charging connector to use CHAdeMO stations. |
| The Combo Charging System was developed by the SAE J1772 committee as the SAE-standard for DC fast charging. This is clearly the normal J1772 plug plus two larger pins that carry the DC charging current. The CCS standard has been implemented by automakers based in North America (except Tesla) and Europe. However not every electric car sold in North America and Europe supports CCS. The cars with CHAdeMO do not support CCS, and Tesla cars sold in at least North America do not support CCS. | |
 |
This is the socket which matches the CCS plug. |
 |
The Combo 2 plug, implementing the Combo Charging System using the IEC Type 2 plug. This charging connector is widely used in at least Europe for DC fast charging. |
 |
In some markets Tesla uses the IEC Type 2 plug (for the Model S and Model X), or the Combo 2 plug (for the Model 3) as shown here. In those markets the Mobile Connector, Wall Connector, and Destination Chargers all use IEC Type 2 plugs, and can be used by non-Tesla cars for AC charging. The Supercharger stations in those markets have a mix of IEC Type 2 and Combo 2 plugs. In no case does Tesla allow cars with Combo 2 CCS charging ports use Supercharger stations. |
CHAdeMO and CCS are frequently deployed together

While the CHAdeMO and ComboCharging System is not compatible with each other, the charging station manufacturers all sell units that support both protocols.
Stations that support multiple charging protocols look like this, with one cord for each supported electric car charging protocol. In this case one plug is for CHAdeMO, and the other for the Combo Charging System. In Europe where there are additional choices such as 3-phase AC charging, the stations might have 3 or 4 cords.


